
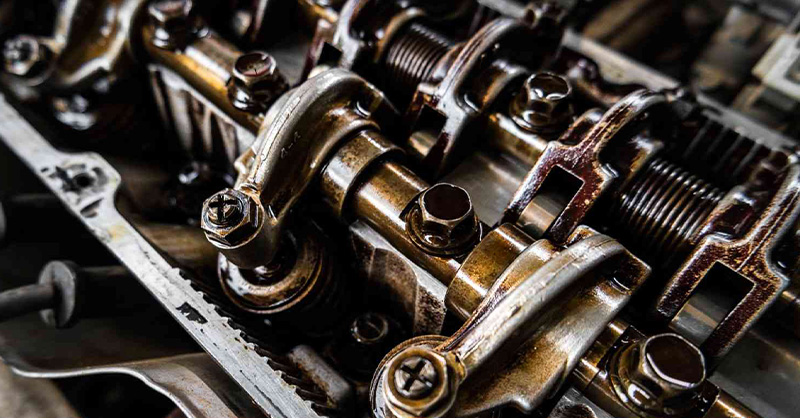
A rocker arm in engine is a lever-like component that transfers motion from the camshaft to the engine valves, controlling when intake and exhaust valves open and close. The rocker arm assembly consists of several parts including the rocker arm itself, rocker arm shaft, fulcrum, and adjustment mechanisms. These components work together to convert the camshaft's rotating motion into the up-and-down movement needed to open valves at precise times. Understanding how rocker arms function is essential for maintaining optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and longevity.
The rocker arm in engine serves as a critical bridge between the camshaft and the valves. Think of it as a seesaw that rocks back and forth. When the camshaft pushes one end up, the other end pushes down on the valve stem, opening the valve. This simple yet ingenious mechanism has been used in engines for decades.
Made typically from hardened steel or aluminum alloys, rocker arms must withstand tremendous forces and heat. They operate thousands of times per minute in a running engine, making durability and precision absolutely essential. Modern rocker arms are engineered to handle these demanding conditions while minimizing friction and wear.
The positioning of the rocker arm in engine design varies depending on the engine type. In overhead valve (OHV) engines, rocker arms sit above the valves in the cylinder head. In overhead cam (OHC) engines, they're positioned directly under the camshaft, creating a more compact and efficient design.
The rocker arm assembly is more than just a single component. It's a carefully designed system of parts that work in harmony. Let's break down what makes up this essential assembly.
Key Components of the Assembly
Not all rocker arms are created equal. Different designs offer various advantages depending on the engine's purpose and performance requirements.
GPP India specializes in manufacturing high-quality roller rocker arms that meet international standards. The precision engineering involved in roller designs makes them the preferred choice for both performance enthusiasts and manufacturers seeking reliability.
Rocker arms can also be classified by how they're mounted:
Understanding the function helps appreciate the engineering behind these components. Let's walk through what happens during engine operation.
1. The Four-Stroke Cycle
In a typical four-stroke engine, the rocker arm in engine plays a vital role in each cycle:
2. The Importance of Rocker Arm Ratio
The rocker arm ratio refers to the relationship between the two arms of the lever. A 1.5:1 ratio means the valve opens 1.5 times more than the amount the pushrod or cam lobe lifts the rocker arm. Higher ratios (like 1.6:1 or 1.7:1) increase valve lift without changing the camshaft. This can improve airflow and power, but it also increases stress on the valve train. Engine builders carefully select rocker arm ratios to match their performance goals.
Like any mechanical component, rocker arms can develop problems over time. Recognizing these issues early can save you from expensive repairs.
1. Wear Patterns and Their Causes: Rocker arms wear where they contact other components. You might notice grooves on the valve stem contact point or on the side that touches the pushrod. This wear happens naturally but accelerates if:
Regular oil changes with quality lubricant help minimize wear. GPP India recommends following manufacturer service intervals to maximize rocker arm assembly life.
2. Noise Diagnosis: A clicking or tapping noise from the valve cover area often indicates rocker arm problems. The sound usually means:
Adjusting valve lash is a routine maintenance task that many car owners can learn to do themselves. However, worn components need replacement to restore quiet operation.
3. Lubrication Requirements: The rocker arm assembly depends entirely on proper lubrication. Oil must reach all moving parts through passages in the cylinder head and rocker arm shaft. When oil flow is restricted:
Modern engines use pressurized oiling systems that force oil to the rocker arms. Older engines might use splash lubrication, which is less reliable. Either way, maintaining clean oil at the correct level is non-negotiable.
For those looking to extract more power from their engines, the rocker arm assembly offers opportunities for improvement.
When upgrading, ensure the new rocker arms match your engine's specifications. The wrong ratio or geometry can cause valves to hit pistons or fail to open fully.
2. Matching Components: The rocker arm assembly doesn't work in isolation. It must be matched with:
Performance engine builds require careful selection of all valvetrain components. This is where consulting with experienced builders or manufacturers like GPP India becomes valuable.
The materials and processes used to create rocker arms significantly impact their performance and durability.
1. Steel Alloys: Most rocker arms use various steel alloys chosen for their properties:
Heat treatment processes strengthen steel rocker arms, creating a hard surface layer while maintaining a tough core. This combination resists wear while preventing brittle fractures.
2. Aluminum Advantages: Aluminum rocker arms weigh roughly half as much as steel versions. This weight reduction allows:
However, aluminum is softer than steel, so these rocker arms typically feature steel inserts at wear points. The combination gives you lightweight performance with good durability.
3. Manufacturing Precision: Modern CNC machining creates rocker arms with incredible accuracy. Tolerances measured in thousandths of an inch ensure:
Quality manufacturers invest in precision equipment and rigorous quality control. This attention to detail separates professional-grade components from budget alternatives.
Proper installation ensures your rocker arm assembly performs as designed. Here's what you need to know.
Always refer to your engine's specifications for correct lash settings. Different valves may require different clearances.
1. Torque Specifications
Rocker arm mounting bolts or nuts must be tightened to precise torque values. Over-tightening can crack castings or distort the rocker arm shaft. Under-tightening allows movement that causes wear and loosening.
Use a quality torque wrench and follow the engine manufacturer's specifications. Tighten bolts in the recommended sequence to ensure even pressure distribution.
2. Break-In Procedure
New rocker arms need a proper break-in period. The initial hours of operation allow surfaces to mate and wear patterns to establish. During break-in:
GPP India's high-quality rocker arms are manufactured to tight tolerances, but break-in is still important for maximum longevity.
Engine technology constantly evolves, and rocker arm design advances along with it.
With so many options available, how do you select the best rocker arm in engine for your application?
1. Consider Your Engine's Purpose
1. Quality Indicators
Look for these signs of quality rocker arms:
Budget parts might save money initially, but often cost more in the long run through poor performance, increased wear on other components, or premature failure.
The rocker arm in engine might seem like a simple component, but as we've explored, it plays a crucial role in engine performance, efficiency, and reliability. From basic stamped steel designs to advanced roller rocker arms with needle bearings, these components have evolved significantly over the years.
Understanding your rocker arm assembly helps you maintain your engine properly and make informed decisions about repairs or upgrades. Whether you're keeping a daily driver running smoothly or building a high-performance engine, choosing quality components from manufacturers like GPP India ensures you get the performance and longevity you need.
Remember that the valve train is a system where all components must work together harmoniously. The best rocker arms in the world won't compensate for worn valve guides, weak springs, or an inappropriate camshaft. Take a holistic approach to valve train maintenance and upgrades for optimal results.
Rocker arm failure typically results from inadequate lubrication, excessive valve lash, using incorrect rocker arm ratios, or running the engine at higher-than-designed RPM levels. Regular maintenance and proper oil changes prevent most failures.
While technically possible, mixing rocker arm types isn't recommended. Different designs have varying weight and friction characteristics that can cause imbalanced valve train operation. Use matched sets for best results.
During regular valve adjustments (typically every 30,000-60,000 miles for solid lifter engines) or whenever you hear unusual noise from the valve train. Race engines require inspection after every event or season.
Roller rocker arms need the same quality oil and proper clearances as standard rocker arms. However, the roller bearings benefit from oil with appropriate anti-wear additives. Follow manufacturer recommendations for best results.
Rocker arm ratio is the mechanical advantage of the lever, while lift is the total distance the valve opens. Ratio multiplied by cam lobe lift equals valve lift. For example, a 0.300-inch cam lobe with 1.5:1 rocker arms produces 0.450-inch valve lift.
Yes, quality aluminum rocker arms work excellent in street applications. They offer durability comparable to steel while reducing valve train weight. Ensure they have steel inserts at wear points for maximum longevity.
Check for adequate piston-to-valve clearance when the engine is assembled. The rocker arms should move smoothly without binding, and valves should open to the specification provided by the camshaft manufacturer. Professional engine builders verify geometry using specialized checking tools.
Not directly, but severe wear in the rocker arm assembly can allow excessive oil leakage at the pivot points. This can contribute to lower oil pressure readings, especially at idle. Fix worn components promptly to maintain proper oil pressure throughout the engine.